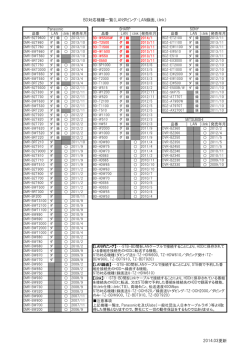
[4]IAEAベンチマーク(EBR-II LOF,ULOF Tests)
Benchmark Analyses for EBR-II LOF and ULOF Tests Severe Accident Evaluation Prof. Hiroyasu MOCHIZUKI (URL) http://www.m.npes.u-fukui.ac.jp/mochizuki.html 1. Background -21 Natural circulation tests with and without scram were conducted using EBR-II reactor. Test results are proposed as benchmark problems through IAEA. The mechanism of negative reactivity insertion is investigated using the NETFLOW++ code which has been validated using the data measured in various fast reactors. The following organizations are participating in the benchmark. ANL (USA),Tera Power(USA),IRSN(France), IGCAR (India), KAERI (Korea), XJTU (China), UNIPI(Italy), KIT(Germany), PSI(Switzerland), JAEA (Japan), and Mochizuki Lab. of Univ. Fukui, and others. 6.369 -1 3. Analysis model and conditions ●Flowrate and temperature on the secondary side of IHX are given as boundary conditions. ●SHRT-17: Power is also boundary condition. ●Neutronic characteristics are calculated by the ERANOS code for the SHRT-45R (1-point kinetics and reactivities). ● Uniform geometry change of the core is assumed in the neutronics calculation. 4. Results 5.827 IHX Pump Valve Pump 5.369 4.520 2.656 [18] [16] 1.182 [17] 9 [11] [19] 1.867 [21] Na:340m3 2.092 4 2.232 Leak 5 4.297 3.694 EMP 6 1.198 3 1.655 [9],[10] -0.065 [1]~[8] -0.078 [20] -0.865 [14] [15] 1 High pressure prenum -1.304 2 Low pressure plenum [12] 8 --1.551 [13] [18] Equivalent pipe having full areal of sodium [19] Equivalent pipe having half of the sodium area [12], [13] Equivalent pipe having 1/4 of the sodium area Fig. 2 NETFLOW++ calculation model of the EBR-II primary Fig. 1 Schematic of EBR-II 900 Core top (TTC-8) (Measured) Mid core (MTC-20) (Measured) High-pressure plenum (Measured) Core top (Calculated) Mid core (Calculated) High-pressure plenum (Calculated) 850 Temperature (K) 900 0.3 Core top (TTC-2) (Measured) Mid core (MTC-4) (Measured) Core top (Calculated) Mid core (Calculated) 800 0.25 800 0.2 XX10 Flowrate (Measured) XX10 (Calculated) 750 0.15 700 0.1 650 0.05 700 600 600 0 200 400 600 800 0 200 400 600 0 800 Time (s) Time (s) Fig. 3 Comparison between measurement and calculation of SHRT-17 test (Left: high power channel, Right: Stainless steel subassembly) Table 1,2 Neutron characteristics and various reactivities analyzed by ERANOS Delayed neutron group 1 2 3 4 5 6 eff Fraction (-) Decay constant (1/s) 1.246870×10-2 3.062465×10-2 1.130473×10-1 3.056735×10-1 1.171473×100 3.129448×100 - 2.183285×10-4 1.458326×10-3 1.334071×10-3 2.695671×10-3 8.615698×10-4 3.063377×10-4 6.874304×10-3 Item Doppler Axial expansion Radial expansion Sodium density core only Sodium density all Control rod expansion pcm/K (=10-5/K) -0.024 -0.84 -2.10 -0.71 -1.90 0.0 3.876173×10-7 sec Neutron life time: 50 1000 1 ●Fig.3 shows a comparison between measurement and calculation of SHRT-17 test. Good agreement is obtained in spite of the blind calculation result. ●Table 1&2 illustrate 1-point kinetics and reactivities calculated by the ERANOS code. The reactivity relating control rod expansion is not evaluated. ●Fig. 4 illustrates comparison of temperature and flowrate between measurement and calculation for SHRT-45R. This calculation result is obtained when Fig. 4 Comparison of temperature and flow rate in instrumented channel the feedback of -1.26pcm/K for sodium density for SHRT-17 test change is used in the NETFLOW++ code. This value is within the calculated range by the ERANOS code. ●Fig. 5 illustrates the axial temperature distribution in XX09 instrumented channel. ●Fig. 6 shows the breakdown of reactivities in the SHRT-45R test. The Doppler reactivity is rather small compared to that of the usual fast reactor due to small amount of U238 in the core. The largest contribution is the radial expansion, and the second is Fig. 5 Axial temperature distribution in SHRT-45 Fig.6 Reactivities in SHRT-45 the reactivity due to sodium density change. 800 700 40 30 0 200 400 600 800 0.6 20 0.4 10 0.2 0 600 0.8 XX09 (Measured) XX09 (Calculated) 0 200 400 600 800 XX09 flowrate (kg/s) Primary pump #2 flowrate (kg/s) Temperature (K) Primary pump #2 (Measured) Primary pump #2 (Calculated) Core top (TTC-8) (Measured) High-pressure plenum (Measured) Core top (Calculated) High-pressure plenum (Calculated) 900 0 Time (s) Time (s) 0.1 1000 0 -0.1 Pellet center at 0 s Coolant at 0 s Pellet center at 70 s Coolant at 70 s 800 Reactivity ($) Temperature (K) 900 Net reactivity Doppler Coolant density Radial expansion Axial expansion -0.2 -0.3 -0.4 700 -0.5 600 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 Height from bottom of the core (m) 0.5 0.6 -0.6 0 200 400 600 800 Time (s) Conclusions XX10 flowrate (kg/s) 1000 Temperature (K) Link 1: XX09, Link 2: ½ D in row 1‐3 Link 3: D in row 3‐4 Link 4: D in row 5 Link 5: D in row 6‐7 Link 6: SRs and CRs Link 7: Steel SA in row 1‐5 including XX10 Link 8: Reflector in row 7 Link 9: Outer reflector Link 10: Blanket [22] 7 [24] [23] 2. Heat Removal Test at EBR-II ● Fig. 1 shows schematic of the primary system of the EBR-II reactor. The core, pumps and an intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) are connected by piping, and all these components are in a sodium tank. ●Metal fuels are loaded. ●Two kinds of tests, natural circulation (NC) with scram (SHRT-17), and NC without scram (SHRT-45R) were benchmark problems. 6.369 -2 H. Mochizuki, K. Muranaka, T. Asai, and W.F.H. van Rooijen, Benchmark Analyses for EBR-II Shutdown Heat Removal Tests SHRT-17 and SHRT-45R, Nuclear Engineering and Design, 275, (2014), pp.398-407. The thermalhydraulic calculation model of the NETFLOW++ code is verified through the calculation of the SHRT-17 test. It is estimated that the reactivity feedback for the SHRT-45R test is caused by the geometry change of the reactor core and sodium density change, especially by the radial expansion of the fuel, and the Doppler feedback is rather small. Reactivity calculated by the ERANOS code is proper which traces the peak temperature behavior. When the absolute value of the feedback of the sodium density change is tuned within the calculated range. EBR-II炉で行われたLOFとULOF試験のベンチマーク解析 – IAEA CRPベンチマーク – 原子力シビアアクシデント評価部門 【特命教授】 望月弘保 (URL) http://www.m.npes.u-fukui.ac.jp/mochizuki.html 1. 背景 -21 EBR-II高速炉を用いて、スクラム後およびスクラム無し での自然循環熱除去試験が行われ、熱除去が達成され たメカニズムを解析する問題がIAEAより出された。これ までに種々の原子炉のデータを用いて検証してきた NETFLOW++コードを用いてメカニズムを解析する。 参加している国と主な機関: (アメリカ合衆国)アルゴンヌ国立研究所ANL、テラパ ワー、(フランス)IRSN、(インド)インディラ・ガンジー原 子力研究センターIGCAR、(韓国)原子力研究所KAERI、 (中国)西安交通大学XJTU、(日本)原子力研究開発機 構JAEA、福井大望月研究室、(ドイツ)KIT、(イタリア) ピサ大学、(スイス)PSI 6.369 -1 [18] [16] 1.182 4.297 2.092 [17] 9 [11] [19] 1.867 [21] Na:340m3 6 1.198 3 1.655 [9],[10] -0.065 -0.078 [1]~[8] [20] -0.865 [14] [15] 1 High pressure prenum -1.304 2 Low pressure plenum [12] 8 --1.551 [13] [18] Equivalent pipe having full areal of sodium [19] Equivalent pipe having half of the sodium area [12], [13] Equivalent pipe having 1/4 of the sodium area 図2 NETFLOW++を用いたEBR-II 1次系の解析体系 図1 EBR-IIの原子炉概要 900 0.3 Core top (TTC-2) (Measured) Mid core (MTC-4) (Measured) Core top (Calculated) Mid core (Calculated) 800 0.25 800 0.2 XX10 Flowrate (Measured) XX10 (Calculated) 750 0.15 700 0.1 650 0.05 XX10 flowrate (kg/s) 850 Temperature (K) 900 Temperature (K) 4.520 3.694 4 2.232 Leak 5 Core top (TTC-8) (Measured) Mid core (MTC-20) (Measured) High-pressure plenum (Measured) Core top (Calculated) Mid core (Calculated) High-pressure plenum (Calculated) 700 600 0 200 400 600 800 0 200 400 600 0 800 Time (s) Time (s) 図3 SHRT-17での計測結果と解析結果の比較(左図:高出力チャンネル、右:ス テンレス集合体) 表1,2 ERANOSコードで解析した動特性パラメータと反応度係数 Decay constant (1/s) 1.246870×10-2 3.062465×10-2 1.130473×10-1 3.056735×10-1 1.171473×100 3.129448×100 - 2.183285×10-4 1.458326×10-3 1.334071×10-3 2.695671×10-3 8.615698×10-4 3.063377×10-4 6.874304×10-3 1000 pcm/K (=10-5/K) -0.024 -0.84 -2.10 -0.71 -1.90 0.0 Item Doppler Axial expansion Radial expansion Sodium density core only Sodium density all Control rod expansion 3.876173×10-7 sec Neutron life time: 50 Core top (TTC-8) (Measured) High-pressure plenum (Measured) Core top (Calculated) High-pressure plenum (Calculated) 900 800 700 600 0 200 400 600 1 Primary pump #2 (Measured) Primary pump #2 (Calculated) Primary pump #2 flowrate (kg/s) 800 40 0.8 XX09 (Measured) XX09 (Calculated) 30 0.6 20 0.4 10 0.2 0 0 200 400 600 800 0 Time (s) Time (s) 図4 高出力 計測チャンネルの温度と流量の計測データと解析結果の比較 0.1 1000 0 900 -0.1 Pellet center at 0 s Coolant at 0 s Pellet center at 70 s Coolant at 70 s 800 Reactivity ($) Temperature (K) Fraction (-) Net reactivity Doppler Coolant density Radial expansion Axial expansion -0.2 -0.3 -0.4 700 -0.5 600 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 Height from bottom of the core (m) -0.6 0 200 400 600 800 Time (s) SHRT-45での炉心軸方向温度分布 図6 SHRT-45R試験での反応度の変化 H. Mochizuki, K. Muranaka, T. Asai, and W.F.H. van Rooijen, Benchmark Analyses for EBR-II Shutdown Heat Removal Tests SHRT-17 and SHRT-45R, Nuclear Engineering and Design, 275, (2014), pp.398-407. EBR-IIで行われた自然循環熱除去試験を解析した。LOF試験結果は、NETFLOW++コードで非常に精度よく解析できた。 EBR-IIでのULOF試験で炉心の出力が低下した原因は、ポンプ停止後の温度上昇による炉心の形状変化とナトリウム密 度の変化であることが分かった。 炉心の形状変化は、燃料下部はほとんど変化せず、上部が大きく変化するが、解析の結果、過渡時の温度分布が、下部 から上部に直線的に変化しているため、均一変化で解析した核特性が近似的に使えたと結論できる。 今後、燃料が上部ほど大きく変化した体系での核計算が必要である。 XX09 flowrate (kg/s) Delayed neutron group 1 2 3 4 5 6 eff ●図3にSHRT-17での高出力チャンネルとステンレ スチャンネルの計測結果との比較を示す。解析結果 は、Blindであったが、単純な自然循環であるため、 両者は良く一致している。 ●表1,2は、ERANOSコードで解析した1点動特性パ ラメータと各種反応度係数を示している。炉心膨張に 伴う制御棒の反応度は未評価であるため、0と仮定。 ●図4は、SHRT-45R試験における、高出力チャン ネルXX09の温度と流量の計測と解析の比較を示す。 ERANOS解析結果のナトリウム密度変化を計算範 囲の-1.26pcm/Kとした時の結果である。このことに よって、均一に炉心が膨張するとして計算した核特 性結果を用いて、プラント熱水力が評価できることが 分かった。 ●図5は、炉心軸方向温度分布 ●図6は、 SHRT-45R試験での反応度の割合を示し ている。燃料にU238 が少ないため、ドプラー反応度 はほとんど無視できる程度に小さい。もっとも大きな 反応度は、燃料の計方向への膨張であり、次がナト 図5 リウムの密度変化となっている。 結 論 5.369 EMP Temperature (K) 4. 結果 Pump 2.656 600 ●IHXの2次側は、流量と温度が与えられている。 ●SHRT-17は、出力が時間の関数で与えられた。 ●SHRT-45Rは、出力を計算しなければならない。 このため、フランスで開発されたERANOSコードを 用いて、1点動特性パラメータと反応度係数を算 出し、NETFLOW++コードで核熱水力解析を実施。 ●燃料温度上昇による燃料膨張は、計方向、軸 方向とも均一と仮定した。 5.827 [24] IHX Pump Valve 1000 3. 解析モデルと条件 Link 1: XX09, Link 2: ½ D in row 1‐3 Link 3: D in row 3‐4 Link 4: D in row 5 Link 5: D in row 6‐7 Link 6: SRs and CRs Link 7: Steel SA in row 1‐5 including XX10 Link 8: Reflector in row 7 Link 9: Outer reflector Link 10: Blanket [22] 7 [23] 2. EBR-II炉での過渡試験の概要 ●EBR-II炉は図1に示すように、炉心とポンプ、中 間熱交換器(IHX)等の機器が配管で結合され、全 ての1次系機器がタンク内に納められている。 ●炉心には、金属燃料が装荷されている。 ●原子炉をスクラムして自然循環で除熱した試験、 SHRT-17とスクラムしないで自然循環で除熱した 試験SHRT-45Rが解析対象である。 6.369 -2
© Copyright 2024